Dissolved Air Floation (DAF) Systems
 Dissolved Air Floation (DAF) is used in the water treatment process to remove fine particulate matter from drinking water. The method uses a stream of well-distributed micro-bubbles to capture flocculated particulates. The flocculation stage of the DAF treatment system uses standard methods of dosing with a variety of mixers and flocculation tank forms. Dissolved Air Floation (DAF) is used in the water treatment process to remove fine particulate matter from drinking water. The method uses a stream of well-distributed micro-bubbles to capture flocculated particulates. The flocculation stage of the DAF treatment system uses standard methods of dosing with a variety of mixers and flocculation tank forms.
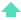
DAF systems typically have a common footprint containing a Flocculation Zone, Inlet Zone, Reaction Zone (where the micro-bubbles capture the floc) and a Floatation Zone (where the floc blanket is floated on the surface and is periodically skimmed off, using mechanical or hydraulic de-sludging). Clarified water migrates through a different route in the base of the DAF floation zone, having been separated from most of its particulate matter.
 Some DAF units exhibit under-performance in the removal of particulate matter and often this can be due not only to problems in the highly complex flow field in local regions around the reaction zone, but can be generated by upstream hydraulic problems which result in un-balanced flow with resultant overloading of particular DAF streams. Some DAF units exhibit under-performance in the removal of particulate matter and often this can be due not only to problems in the highly complex flow field in local regions around the reaction zone, but can be generated by upstream hydraulic problems which result in un-balanced flow with resultant overloading of particular DAF streams.
CFD can be used to gain an understanding of flow patterns in the reaction zone. Modeling the bubble field as a two-phase or drift-flux flow provides an effective way to study flow patterns that can have a significant influence on system performance.
Staff at CFD Solutions Ltd have used CFD to correct problems related to DAF components including the flocculation/mixing-zone, inlet system flow-splits, interior baffle layouts, reaction-zone, floatation-zone and micro-bubble nozzle design.
|


